Expand Your Knowledge
Our resource center archives our case studies, published articles, blogs, webinars, and image galleries. Discover ways microscopy has made a meaningful impact.
With over 35 years of experience in material testing, our scientists have dealt with a wide variety of materials including polymers, coatings, paints, metals, fillers, minerals, composites, pharmaceutical ingredients, solvents, contaminants, impurities and unknowns.
Within our 14,000 square foot facility, we offer microscopy and spectroscopy capabilities to characterize different materials. Our material scientists have knowledge and experience in a wide range of industries including aerospace, automotive, chemical, oil and gas, polymers and plastics, packaging, adhesives, medical devices, textiles and apparel, building materials, electronics, composites, consumer products and nanomaterials.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is one of the most important and versatile techniques for material testing and characterization.
SEM offers high resolution imaging capability and when coupled with energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDS), it provides pinpoint elemental composition for material analysis.
With advanced application, it can also perform elemental x-ray mapping.
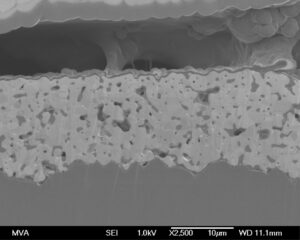
SEM imaging of a polished cross section material
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is useful for testing and characterizing different materials at a near-atomic level, including polymers, nanoparticles and coatings.
TEM is especially useful for characterizing copolymer blends to see how well the different polymers are mixed.
In addition, TEM can achieve much higher resolution than SEM, which makes it a valuable technique for nanoparticle size distribution measurement.
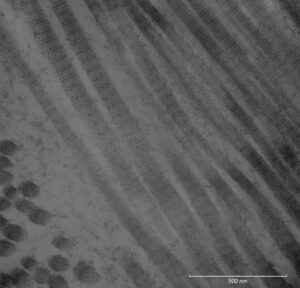
TEM imaging of tissue material
Raman spectroscopy is useful for characterizing materials including nanoparticles, active pharmaceutical ingredients and raw materials, polymers, coatings, and impurities. Raman spectroscopy gives molecular structure and crystallinity information on a material. When coupled with Raman chemical imaging, it can provide molecular information on a pharmaceutical formulation for tablets, stents, inhalants, and different layers of coatings in a packaging material.
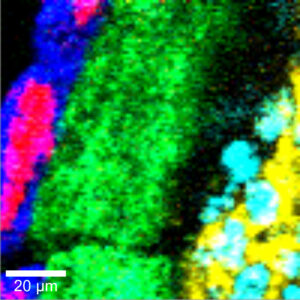
Raman chemical imaging of a drug formulation
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is one of the most robust techniques for material testing. FTIR is extremely useful for material identification and analysis of molecular functional groups.
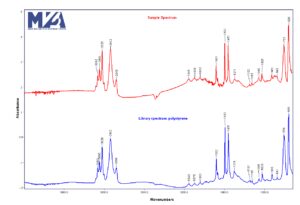
Comparison of an unknown sample to a reference spectrum from the FTIR library
Surface measurement, also known as surface metrology, refers to the measurement of topography or surface roughness of precision surfaces. Interference microscopy is a non-contact optical profilometry technique used to obtain three-dimensional images and quantitative measurement of surface texture or “roughness.”
Surface measurements include surface shape, surface finish, surface profile roughness, surface texture and structural characterization. Surface roughness and the details of the surface profile determine the performance and appearance of many products. The roughness or texture of a part is important for a surface’s suitability in different applications.
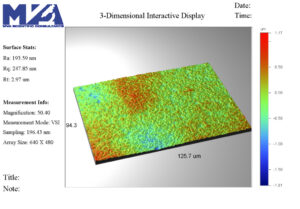
Surface roughness analysis of material
MVA Scientific Consultants has solved thousands of interesting and challenging problems. Our philosophy has always been to provide clients with the highest quality data that will be valuable in helping them solve their issues.
To learn more about how MVA Scientific Consultants’ material analysis and material characterization services can handle your specific needs, contact us today at info@mvainc.com or 770-662-8509.