
Expand Your Knowledge
Our resource center archives our case studies, published articles, blogs, webinars, and image galleries. Discover ways microscopy has made a meaningful impact.

Asbestos fiber release studies are very useful in determining potential asbestos exposure that could occur when someone works with an asbestos-containing product or material. A fiber release study can be used to determine the nature and amount of fibers released during a particular activity. This blog briefly summarizes the results of an in-house study of asbestos fiber release during the preparation of asbestos filters or “mats” from Gooch filter fiber (asbestos).
Francis A. Gooch first proposed the use of a “mat” of asbestos in a special container called a Gooch crucible in 1878 as part of a routine scientific test know as gravimetric analysis. The use of asbestos was novel and clearly superior in accuracy to the alternative filter papers, sand filters and porous cones typically used, mainly due to the asbestos fibers’ resistance to heat.
The mats in this MVA study were prepared using “Powminco Gooch Filter Fiber” – a blend of amphibole asbestos mined by the Powhatan Mining Company and distributed by J.T. Baker.
During the experiment, a certified industrial hygienist (CIH) wore standard air filter cassettes to collect the released particles. The CIH transferred asbestos fibers from the original metal container into metal pans using forceps. After enough material was collected to cover the bottom of a pan, the contents were pressed by hand to form a mat.
A background sampling of the chamber was collected prior to the experiment.
The fibers in the container were examined by multiple methods to determine the types and amounts of asbestos present, in addition to the overall fibrous nature of the material. The air samples collected during the study in the breathing zone of the CIH were also analyzed using test methods developed by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
The results show the Powminco sample contains approximately 98% amphibole asbestos (tremolite/actinolite and possible anthophyllite) as determined by polarized light microscopy (PLM) analysis. The remaining trace (<1%) to 2% consists of talc and rust particles, most likely from the container.
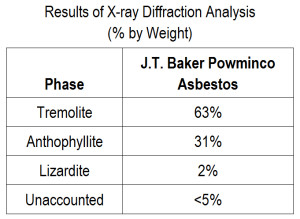
Bulk X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis reports a composition of 63% tremolite, 31% anthophyllite, 2% lizardite, and <5% unknown.
Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) results were useful in representing the asbestiform nature of the sample, which is characterized by long, thin, flexible fibers. Fibers consistent in elemental composition with tremolite and anthophyllite/talc were identified by SEM-EDS.
A transmission electron microscope (TEM) capable of electron diffraction (SAED) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis confirmed the presence of both anthophyllite and tremolite asbestos in the bulk sample. Within the first 20 fibers observed, aspect ratios (length:width) ranged from 11:1 to 127:1 with an average width of 0.9 micrometers.

TEM image of Powminco Gooch Filter Fiber
Phase contrast microscopy (PCM) found the fiber levels in the personal air samples ranged from 1.0 to 1.2 fibers per cubic centimeter (F/cc). A TEM examination of the personal air sample showed that 93% of the PCM-sized fibers collected in the personal air samples were asbestos.
This study concluded that the Powminco Gooch Filter Fiber sample contained both anthophyllite and tremolite asbestos fibers as determined through the combination of PLM, SEM-EDS, TEM-SAED-EDS and XRD techniques. Asbestos fibers released into the breathing zone of a worker during the preparation of Gooch filter mats were at levels of approximately 0.9 to 1.1 asbestos fibers per cubic centimeter, based on personal air sample analyses.
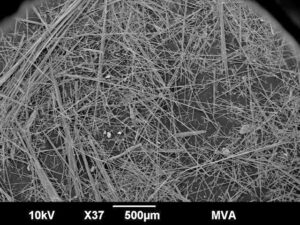
SEM image of Powminco Gooch Filter Fiber
Source: Airborne Asbestos Exposure from Gooch Fiber Use – S.P. Compton and J.R. Millette – MVA Scientific Consultants – THE MICROSCOPE Vol. 60:4, pp 165-170 (2012)
Our resource center archives our case studies, published articles, blogs, webinars, and image galleries. Discover ways microscopy has made a meaningful impact.

